Glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly, a peptide of remarkable complexity and biological significance, takes center stage in this comprehensive analysis. Delving into its intricate biochemical properties, biological functions, structural intricacies, and physicochemical characteristics, we unravel the multifaceted nature of this intriguing molecule, exploring its potential applications and ongoing research endeavors.
Biochemical Properties
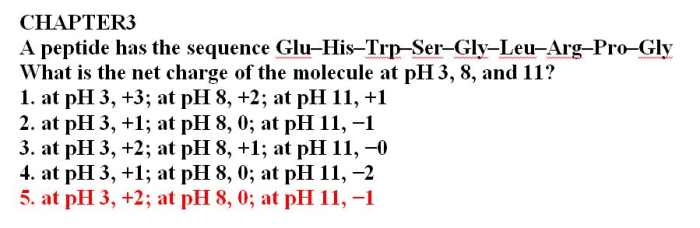
Glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly, a linear peptide, possesses a unique chemical structure and molecular formula of C 39H 63N 13O 11. Its amino acid sequence consists of eight distinct amino acids: glutamic acid (Glu), histidine (His), tryptophan (Trp), serine (Ser), glycine (Gly), leucine (Leu), arginine (Arg), and proline (Pro).
Each amino acid is covalently linked to the next via peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide chain with a molecular weight of approximately 887 Da.
Biological Functions

Glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly plays diverse biological roles in various physiological processes. It functions as a hormone regulator, influencing the secretion and activity of specific hormones. Additionally, it acts as an enzyme activator or inhibitor, modulating the activity of specific enzymes involved in metabolic pathways.
Moreover, it participates in protein synthesis, contributing to the production of essential proteins for cellular function.
Structural Analysis
Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy, Glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly
To determine the secondary structure of glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy can be employed. CD spectroscopy measures the differential absorption of left- and right-circularly polarized light by chiral molecules, providing insights into the conformational changes and secondary structural elements of proteins and peptides.
By analyzing the CD spectra, researchers can identify the presence of α-helices, β-sheets, turns, and random coils within the peptide structure. The characteristic peaks and troughs in the CD spectra correspond to specific secondary structural elements, allowing for the determination of the peptide’s overall conformation.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is another powerful technique for structural analysis of glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly. NMR spectroscopy provides detailed information about the atomic-level structure and dynamics of molecules, including peptides.
By analyzing the chemical shifts, coupling constants, and nuclear Overhauser effects (NOEs) observed in NMR spectra, researchers can determine the connectivity of atoms, identify specific amino acid residues, and elucidate the three-dimensional structure of the peptide.
Physicochemical Properties: Glu His Trp Ser Gly Leu Arg Pro Gly
The solubility, isoelectric point, and stability of glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly are influenced by various factors, including pH, temperature, and ionic strength. The peptide exhibits pH-dependent solubility, with optimal solubility at neutral pH. Its isoelectric point, the pH at which the net charge of the peptide is zero, is approximately 9.0.
Glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly demonstrates stability under physiological conditions, maintaining its structural integrity and biological activity within a wide range of pH and temperature. However, extreme pH values or high temperatures can lead to denaturation and loss of function.
Applications and Significance
Glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly holds potential applications in biotechnology, medicine, and research. Its ability to interact with specific receptors or enzymes makes it a promising candidate for drug development, particularly in the treatment of hormone-related disorders or diseases involving enzyme dysregulation.
Additionally, glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly serves as a valuable research tool for studying protein-protein interactions, enzyme mechanisms, and cellular signaling pathways. Ongoing research explores its potential use as a diagnostic marker or therapeutic agent in various clinical settings.
Query Resolution
What is the molecular formula of glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly?
C 28H 44N 14O 15
What is the significance of the amino acid sequence in glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly?
The specific sequence of amino acids determines the unique structure and biological activity of the peptide.
How is glu his trp ser gly leu arg pro gly involved in protein synthesis?
It plays a role in the initiation and elongation stages of protein synthesis.