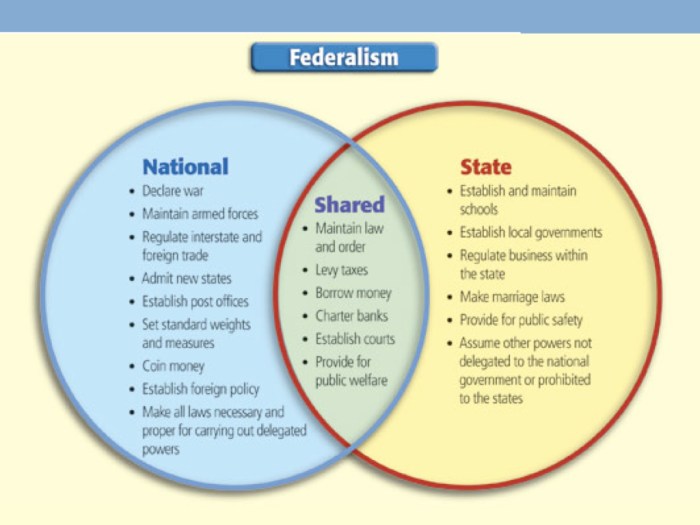
Icivics federalists and anti federalists – In the crucible of America’s founding, the Federalists and Anti-Federalists engaged in a momentous debate that would profoundly shape the nation’s destiny. Their clash of ideas over the nature of government ignited a fierce intellectual battleground, the reverberations of which continue to echo in American politics today.
The Federalists, led by Alexander Hamilton and James Madison, championed a strong central government capable of fostering economic growth and national unity. In contrast, the Anti-Federalists, led by Patrick Henry and George Mason, feared that such a powerful government would erode states’ rights and individual liberties.
Federalists and Anti-Federalists: Icivics Federalists And Anti Federalists
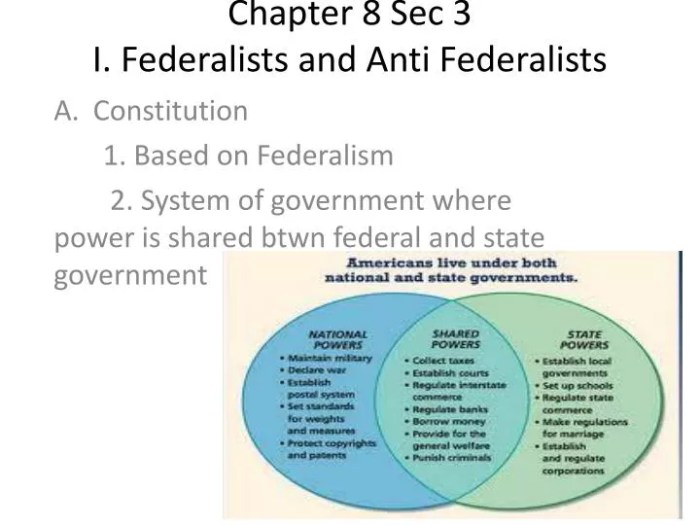
During the formation of the United States, two distinct political factions emerged: the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists. These groups held opposing views on the structure and power of the new federal government.
Federalist Arguments, Icivics federalists and anti federalists
Federalists advocated for a strong central government. They believed that a unified nation would be more prosperous, secure, and efficient than a loose confederation of states. They argued that a central government could regulate commerce, establish a national currency, and provide for the common defense.
- Enhanced economic stability through centralized regulation of commerce
- Strengthened national security through a unified military
- Improved efficiency and coordination through a central authority
Anti-Federalist Arguments
Anti-Federalists opposed a powerful central government. They feared that it would infringe on states’ rights and individual liberties. They believed that the Constitution gave the federal government too much power and that it would lead to tyranny.
- Protection of states’ autonomy and sovereignty
- Preservation of individual rights and freedoms
- Prevention of excessive government overreach
The Debate and Ratification
The debates between Federalists and Anti-Federalists were intense. Federalists emphasized the need for a strong central government, while Anti-Federalists argued for limited federal authority. The ratification process of the Constitution was contentious, with both sides engaging in heated discussions.
- The Federalist Papers: A series of essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay that defended the Constitution
- The Anti-Federalist Papers: A collection of essays written by various authors that opposed the Constitution
- State ratification conventions: Where delegates debated and voted on the Constitution
Impact on American History
The Federalist and Anti-Federalist debate had a profound impact on American history. It shaped the structure and principles of the U.S. government, and it continues to influence political discourse today.
- Establishment of a strong central government with limited powers
- Guarantee of individual rights and freedoms through the Bill of Rights
- Ongoing debates about the balance between federal and state power
FAQ Overview
Who were the Federalists?
The Federalists were a political faction that supported the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. They believed in a strong central government capable of promoting economic growth and national unity.
Who were the Anti-Federalists?
The Anti-Federalists were a political faction that opposed the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. They feared that a strong central government would erode states’ rights and individual liberties.
What were the key arguments of the Federalists?
The Federalists argued that a strong central government was necessary to foster economic growth, protect the nation from foreign threats, and ensure domestic tranquility.
What were the key arguments of the Anti-Federalists?
The Anti-Federalists argued that a strong central government would lead to tyranny, erode states’ rights, and infringe upon individual liberties.