Scatter plots and data study guide answer key, the gateway to unlocking data insights, empower analysts with the tools to visualize and interpret complex relationships between variables. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamentals of scatter plots, equipping you with the knowledge to effectively analyze and comprehend data.
From understanding the concept and purpose of scatter plots to interpreting patterns and trends, this guide covers all aspects of scatter plot analysis. Additionally, it provides valuable tips for creating effective scatter plots and utilizing them in data study guides for optimal data comprehension.
Data Analysis with Scatter Plots
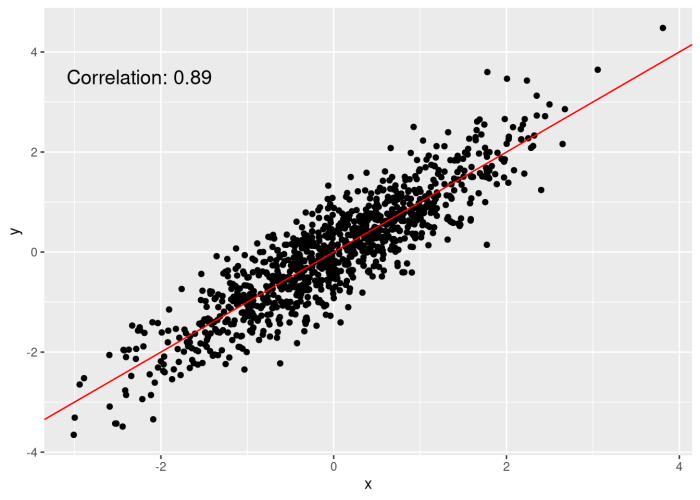
Scatter plots are a powerful data visualization tool that helps us understand the relationship between two or more variables. They are used to identify trends, patterns, and correlations in data, providing valuable insights into the underlying relationships.
Scatter plots consist of a set of points plotted on a graph, where each point represents a pair of data values. The horizontal axis (x-axis) typically represents the independent variable, while the vertical axis (y-axis) represents the dependent variable.
By examining the distribution of points on a scatter plot, we can determine the nature of the relationship between the variables. A positive correlation indicates that as the value of the independent variable increases, the value of the dependent variable also increases.
Conversely, a negative correlation indicates that as the value of the independent variable increases, the value of the dependent variable decreases.
Scatter plots can be used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Identifying trends and patterns in data
- Predicting future outcomes
- Comparing the relationships between different variables
- Identifying outliers and influential points
Interpreting Scatter Plots
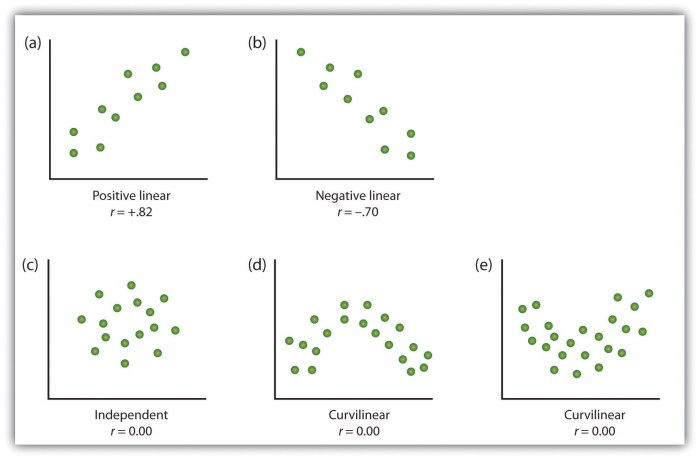
To effectively interpret scatter plots, it is important to understand the patterns and trends they reveal. Here are some key guidelines:
- Identify the overall trend:Look for the general direction of the points. Are they clustered around a line or curve, or are they scattered randomly?
- Determine the correlation:Positive correlations are indicated by points that slope upward from left to right, while negative correlations are indicated by points that slope downward from left to right. The strength of the correlation can be assessed by the tightness of the clustering around the line or curve.
- Identify outliers:Outliers are points that are significantly different from the rest of the data. They can be caused by errors in data collection or by unusual observations.
- Identify influential points:Influential points are points that have a disproportionate effect on the overall trend of the scatter plot. They can be caused by extreme values or by points that are not representative of the majority of the data.
Creating Scatter Plots
Creating scatter plots is a relatively straightforward process that can be done using a variety of software or tools. Here are the steps involved:
- Choose appropriate variables:The variables you choose should be related to each other and should have a meaningful relationship.
- Select a suitable scale:The scale of the axes should be chosen to ensure that the data is displayed clearly and without distortion.
- Plot the points:Each point on the scatter plot represents a pair of data values. Plot the points on the graph, using the x-axis for the independent variable and the y-axis for the dependent variable.
- Label the axes:Clearly label the x- and y-axes with the names of the variables they represent.
- Add a title:Give the scatter plot a descriptive title that summarizes the main finding or purpose of the plot.
Scatter Plots in Data Study Guides
Scatter plots are commonly used in data study guides to help students understand the relationships between variables. Here are some examples of how scatter plots can be used in study guides:
- Illustrating concepts:Scatter plots can be used to illustrate the concepts of correlation, positive and negative relationships, and outliers.
- Providing practice exercises:Study guides may include exercises that require students to interpret scatter plots, identify trends, and draw conclusions.
- Assessing comprehension:Scatter plots can be used to assess students’ understanding of the relationship between variables.
HTML Table for Scatter Plot Data
An HTML table can be used to display scatter plot data in a structured and easy-to-read format. The table should include columns for the following information:
- Variable 1
- Variable 2
- Value 1
- Value 2
The table can be formatted using CSS to ensure that it is responsive and easy to read on different devices.
Bullet Points for Scatter Plot Procedures
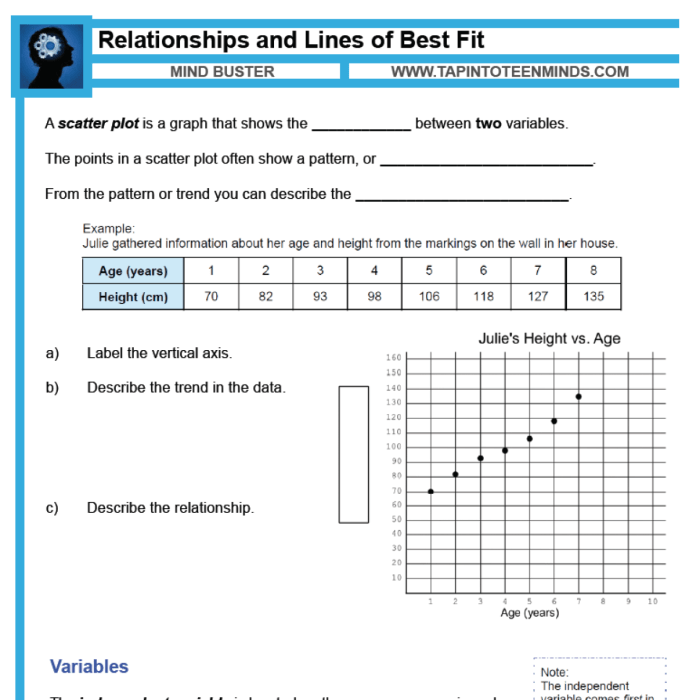
- Identify the variables to be plotted.
- Choose an appropriate scale for the axes.
- Plot the data points on the graph.
- Label the axes and add a title.
- Examine the scatter plot for patterns, trends, and outliers.
- Identify the correlation between the variables.
- Draw conclusions based on the analysis of the scatter plot.
Scatter Plot Illustrations: Scatter Plots And Data Study Guide Answer Key
Here are some examples of different types of scatter plots:
- Positive correlation:A positive correlation is indicated by points that slope upward from left to right. This means that as the value of the independent variable increases, the value of the dependent variable also increases.
- Negative correlation:A negative correlation is indicated by points that slope downward from left to right. This means that as the value of the independent variable increases, the value of the dependent variable decreases.
- No correlation:A no correlation is indicated by points that are scattered randomly around the graph. This means that there is no relationship between the two variables.
- Outliers:Outliers are points that are significantly different from the rest of the data. They can be caused by errors in data collection or by unusual observations.
- Influential points:Influential points are points that have a disproportionate effect on the overall trend of the scatter plot. They can be caused by extreme values or by points that are not representative of the majority of the data.
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of a scatter plot?
Scatter plots are used to visualize the relationship between two numerical variables, allowing analysts to identify patterns, trends, and correlations.
How can I interpret the slope of a scatter plot?
The slope of a scatter plot indicates the strength and direction of the linear relationship between the variables. A positive slope represents a positive correlation, while a negative slope indicates a negative correlation.
What is an outlier in a scatter plot?
An outlier is a data point that significantly differs from the majority of the data points in a scatter plot. Outliers can provide valuable insights but should be interpreted with caution.