A nurse is assessing four clients for fluid balance, a crucial aspect of patient care that involves evaluating a client’s fluid intake and output to ensure proper hydration and electrolyte balance. This assessment is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing complications.
The nurse will consider each client’s unique needs and conditions, employing various assessment techniques to gather accurate data. By interpreting the findings, the nurse can determine if a client is in fluid balance, identify any imbalances, and develop appropriate interventions to address any fluid-related issues.
Nursing Assessment
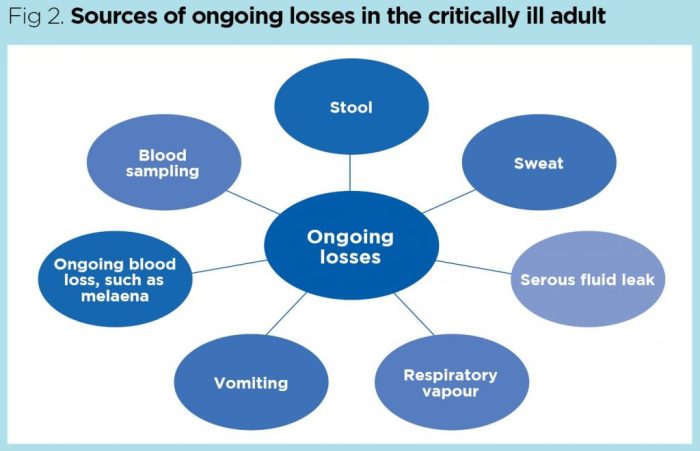
Assessing fluid balance is crucial in nursing as it helps detect and manage imbalances that can lead to severe complications. Signs and symptoms of fluid imbalance include:
- Edema
- Dry mucous membranes
- Oliguria or anuria
- Rapid pulse
- Hypotension
Methods used to assess fluid balance include:
- Physical examination
- Measurement of intake and output
- Laboratory tests
Client Assessment
The four clients being assessed are:
- A 75-year-old male with heart failure
- A 50-year-old female with renal failure
- A 30-year-old male with diabetes
- A 20-year-old female with anorexia nervosa
The rationale for assessing each client’s fluid balance is to:
- Detect early signs of fluid imbalance
- Monitor the effectiveness of treatment
- Prevent complications
The specific parameters that will be assessed include:
- Weight
- Intake and output
- Vital signs
- Skin turgor
- Laboratory values (e.g., serum sodium, potassium)
Fluid Balance Assessment: A Nurse Is Assessing Four Clients For Fluid Balance

Fluid intake can be assessed through:
- Patient self-report
- Observation of fluid intake
- Measurement of fluid intake using a graduated container
Fluid output can be measured through:
- Measurement of urine output
- Measurement of stool output
- Measurement of insensible losses (e.g., through respiration and perspiration)
Tools used to monitor fluid balance include:
- Intake and output charts
- Fluid balance scales
- Laboratory tests
Data Interpretation

Data collected from the fluid balance assessment is interpreted to determine if the client is in fluid balance. Criteria for determining fluid balance include:
- Weight is stable
- Intake and output are equal
- Vital signs are within normal limits
- Skin turgor is good
- Laboratory values are within normal limits
Signs and symptoms that indicate fluid imbalance include:
- Edema
- Dry mucous membranes
- Oliguria or anuria
- Rapid pulse
- Hypotension
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions for clients with fluid imbalance depend on the underlying cause and severity of the imbalance. Interventions may include:
- Restricting fluid intake
- Administering intravenous fluids
- Monitoring intake and output
- Weighing the client daily
- Educating the client about fluid balance
Questions and Answers
What are the signs and symptoms of fluid imbalance?
Signs and symptoms of fluid imbalance can include: dehydration, edema, hypotension, tachycardia, and electrolyte disturbances.
How is fluid intake assessed?
Fluid intake can be assessed by monitoring oral intake, intravenous fluids, and other sources of fluid administration.
What tools are used to monitor fluid balance?
Tools used to monitor fluid balance include: intake and output charts, weight measurements, and physical examination findings.