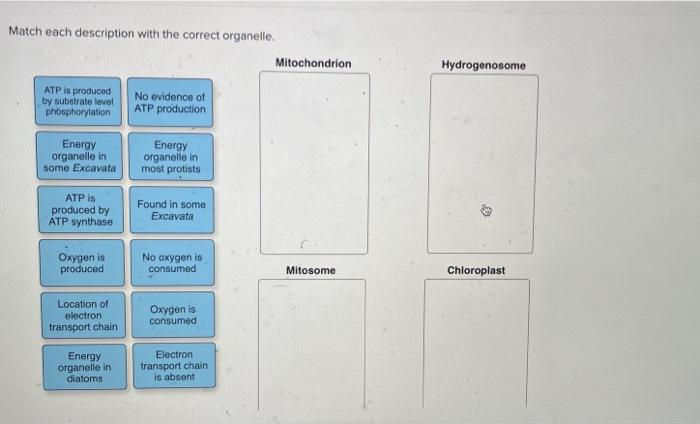
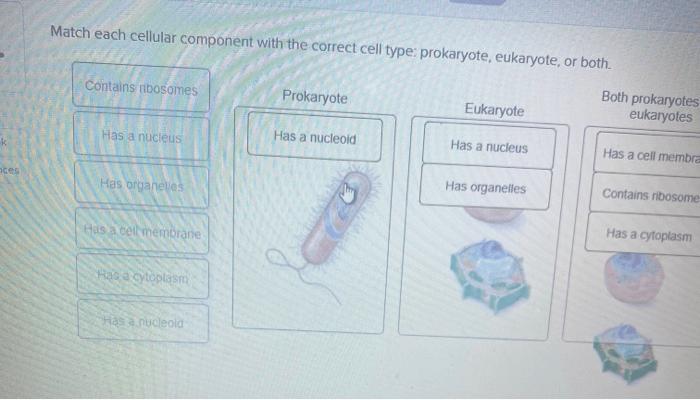
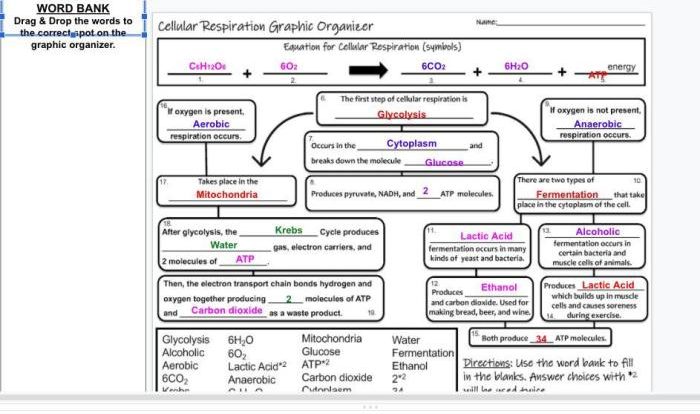
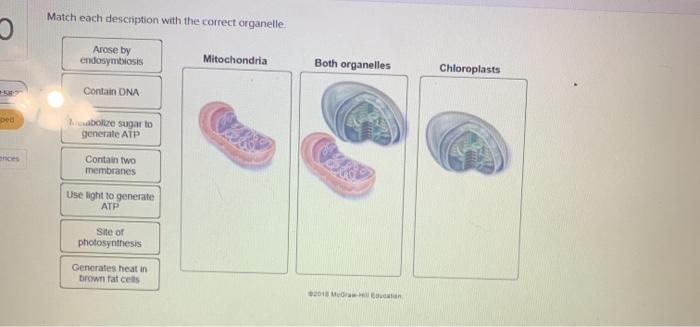
Match each description with the correct organelle embarks on a captivating exploration of the intricate world of organelles, the specialized compartments within cells that perform essential functions. From their unique structures to their intricate interactions, this narrative unravels the mysteries of these cellular marvels, providing a comprehensive understanding of their vital roles in maintaining life.
Organelles, the functional units of cells, exhibit a remarkable diversity in their structures and functions. This diversity is intricately linked to the specific roles they play within different cell types, highlighting the remarkable adaptability of life’s building blocks.
Organelle Structure and Function
Organelles are the specialized compartments within a cell that perform specific functions essential for cellular life. Their structure is intricately adapted to their function, enabling them to carry out their unique roles within the cell.
For example, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. Its extensive surface area provides ample space for these processes. Similarly, the mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, have folded inner membranes that increase their surface area for efficient energy production.
The interdependence of organelles within a cell is crucial for cellular homeostasis. The ER, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes form a secretory pathway, working together to modify, sort, and release proteins.
Organelle Diversity
| Organelle | Primary Function | Example Cells | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitochondria | Energy production | Muscle cells, nerve cells | Provide ATP for cellular activities |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis | Plant cells | Convert light energy into chemical energy |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis | All cells | Essential for cell growth and function |
| Lysosomes | Digestion and waste disposal | White blood cells, macrophages | Break down and remove cellular waste |
Organelle presence and abundance vary across cell types. Muscle cells, for instance, have numerous mitochondria to meet their high energy demands. Plant cells contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, while animal cells do not.
Organelle Interactions
Organelles interact extensively, forming a dynamic network within the cell. The ER communicates with the Golgi apparatus to transport proteins. Mitochondria and the nucleus exchange molecules to regulate cellular metabolism.
These interactions are crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Disrupted organelle interactions can lead to cellular dysfunction and disease. For example, impaired communication between the ER and Golgi apparatus can result in protein misfolding and neurodegenerative disorders.
Organelle Evolution, Match each description with the correct organelle
Organelles are thought to have evolved from symbiotic relationships between ancient prokaryotic cells. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once independent bacteria that were engulfed by larger cells.
Evidence supporting this theory includes the presence of their own DNA, similar to bacterial genomes. Moreover, some organelles, such as peroxisomes, are believed to have evolved from free-living bacteria.
Organelle Imaging Techniques
Various techniques are used to visualize and study organelles. Light microscopy allows for basic organelle observation, while electron microscopy provides ultrastructural details.
Fluorescent microscopy uses fluorescent dyes to label and track organelles in living cells. Advanced techniques like super-resolution microscopy and cryo-electron microscopy enable even higher resolution imaging.
These techniques have revolutionized our understanding of organelle structure and function, providing insights into cellular processes at the nanoscale.
Essential FAQs: Match Each Description With The Correct Organelle
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of cells, responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration.
How do ribosomes contribute to protein synthesis?
Ribosomes are the protein factories of cells, responsible for assembling amino acids into proteins based on the genetic instructions carried by mRNA.