Control of the diameter of the respiratory passages depends upon a complex interplay of physiological mechanisms, neural pathways, and pharmacological interventions. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for airway management, respiratory support, and disease diagnosis.
The diameter of the respiratory passages is regulated by a combination of autonomic nervous system activity, hormonal influences, and local factors such as airway stretch and inflammation.
Control of the Diameter of the Respiratory Passages
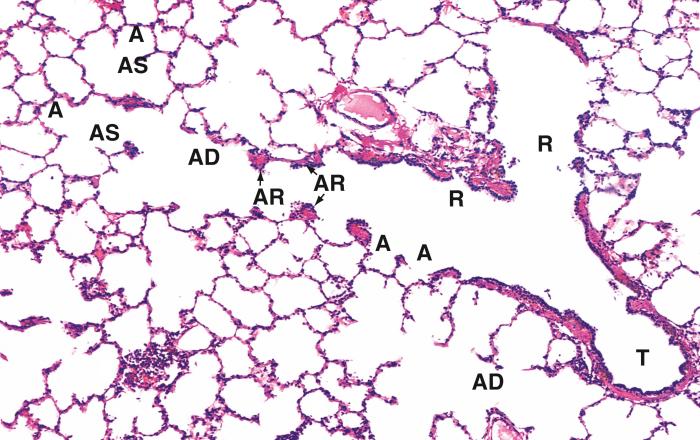
The diameter of the respiratory passages is crucial for maintaining adequate airflow and gas exchange. This diameter is regulated by a complex interplay of physiological mechanisms involving the autonomic nervous system, hormones, and local factors.
Diameter of Respiratory Passages: Regulation Mechanisms
The diameter of the respiratory passages is primarily regulated by the autonomic nervous system, which includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
Sympathetic innervationcauses bronchodilation, while parasympathetic innervationcauses bronchoconstriction. These effects are mediated by the release of neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and norepinephrine.
In addition to the autonomic nervous system, hormones such as epinephrine and histamine can also affect the diameter of the respiratory passages. Epinephrine causes bronchodilation, while histamine causes bronchoconstriction.
Local factors, such as the release of inflammatory mediators, can also influence the diameter of the respiratory passages. These mediators can cause bronchoconstriction or bronchodilation, depending on the specific mediator.
Neural Control of Respiration
The neural control of respiration involves a complex network of pathways that originate in the brainstem and spinal cord and extend to the peripheral nerves.
The brainstemcontains the respiratory centers, which generate the basic rhythm of respiration. These centers are modulated by inputs from the spinal cordand peripheral nerves, which provide information about the status of the respiratory system.
The peripheral nerves that innervate the respiratory muscles are responsible for carrying motor commands from the brainstem to the muscles. These commands control the contraction and relaxation of the muscles, which in turn alters the diameter of the respiratory passages.
Pharmacological Interventions, Control of the diameter of the respiratory passages depends upon
A variety of pharmacological agents can be used to alter the diameter of the respiratory passages. These agents can be used to treat a variety of respiratory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Bronchodilatorsare drugs that cause bronchodilation. They are used to treat conditions that cause bronchoconstriction, such as asthma and COPD.
Bronchoconstrictorsare drugs that cause bronchoconstriction. They are used to treat conditions that require a reduction in airflow, such as severe hemoptysis.
Respiratory Diseases and Diameter Control
A number of respiratory diseases can affect the diameter of the respiratory passages. These diseases can disrupt the normal control mechanisms, leading to bronchoconstriction or bronchodilation.
Asthmais a chronic inflammatory disease that causes bronchoconstriction. This bronchoconstriction is caused by the release of inflammatory mediators, such as histamine and leukotrienes.
COPDis a chronic obstructive lung disease that causes bronchoconstriction. This bronchoconstriction is caused by the narrowing of the airways due to inflammation and mucus production.
Clinical Significance
Understanding the control of respiratory passage diameter is of great clinical significance. This understanding is essential for the management of airway emergencies, the provision of respiratory support, and the diagnosis of respiratory diseases.
By understanding the mechanisms that regulate the diameter of the respiratory passages, clinicians can develop effective strategies for managing respiratory conditions and improving patient outcomes.
Clarifying Questions: Control Of The Diameter Of The Respiratory Passages Depends Upon
What factors regulate the diameter of the respiratory passages?
The diameter of the respiratory passages is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, hormones, and local factors such as airway stretch and inflammation.
How does the autonomic nervous system control respiratory passage diameter?
The autonomic nervous system controls respiratory passage diameter through the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches. The sympathetic nervous system causes bronchodilation, while the parasympathetic nervous system causes bronchoconstriction.
What are some examples of pharmacological agents that can alter respiratory passage diameter?
Examples of pharmacological agents that can alter respiratory passage diameter include beta-agonists, anticholinergics, and corticosteroids.