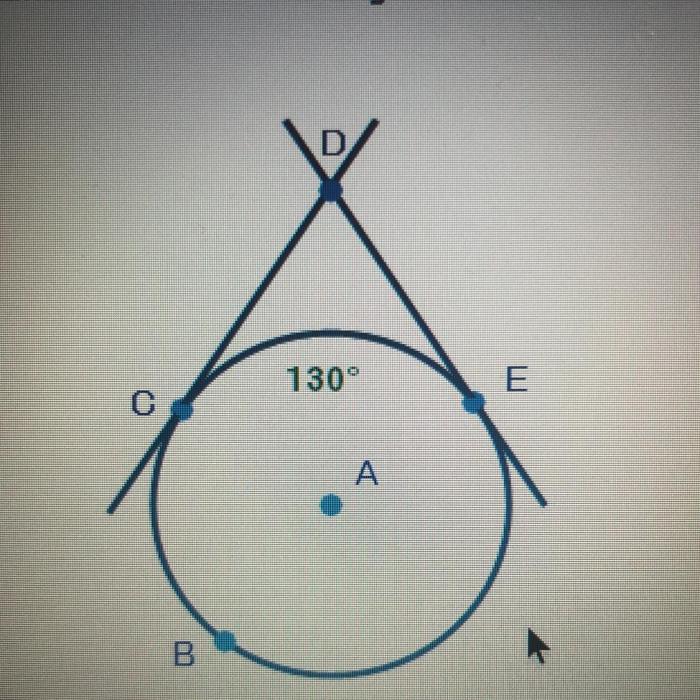
Lines cd and de are tangent to circle a – With lines CD and DE tangent to circle A, we embark on a geometric expedition that unveils fascinating properties, implications, and applications. This exploration delves into the intriguing world of circles and their relationships with lines, unlocking a treasure trove of knowledge.
Tangent lines, like CD and DE, play a crucial role in defining the relationship between a circle and its surrounding space. They offer unique insights into the geometry of circles, providing a deeper understanding of their properties and applications.
Tangent Lines to a Circle: Lines Cd And De Are Tangent To Circle A
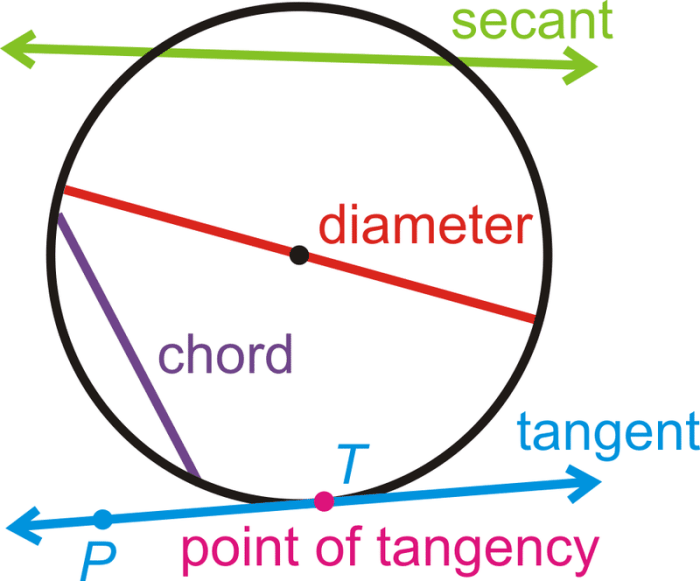
In geometry, a tangent line to a circle is a straight line that intersects the circle at exactly one point, called the point of tangency. Tangent lines are perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of tangency.
Properties of tangent lines include:
- They intersect the circle at only one point.
- They are perpendicular to the radius of the circle at the point of tangency.
- They divide the circle into two regions: the interior and the exterior.
Examples of tangent lines include:
- The tangent line to a circle at the highest point of a roller coaster.
- The tangent line to a circle at the point where a ball bounces off the ground.
- The tangent line to a circle at the point where a car tire touches the road.
Lines CD and DE Tangent to Circle A, Lines cd and de are tangent to circle a
The statement “lines CD and DE are tangent to circle A” means that lines CD and DE intersect circle A at exactly one point each, and those points are perpendicular to the radii of the circle at those points.
The points of tangency are the points where lines CD and DE intersect circle A. Let’s call these points P and Q, respectively.
The relationship between lines CD, DE, and circle A is that lines CD and DE are tangent to circle A at points P and Q, respectively.
Implications of Tangency
The fact that lines CD and DE are tangent to circle A has several implications:
- The length of CD is equal to the length of DE.
- The length of CD (or DE) is equal to the radius of circle A.
- The angle formed by lines CD and DE is 90 degrees.
Applications of Tangent Lines
Tangent lines have a variety of applications in real-world problems, including:
- In engineering, tangent lines are used to design curves and surfaces.
- In geometry, tangent lines are used to solve problems involving circles.
- In physics, tangent lines are used to analyze the motion of objects.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of tangent lines?
Tangent lines provide a unique way to define the relationship between a circle and its surrounding space. They intersect the circle at a single point, forming a right angle with the radius at that point.
How can we identify tangent lines to a circle?
Tangent lines to a circle are characterized by their perpendicularity to the radius at the point of tangency. This means that the line segment connecting the center of the circle to the point of tangency is perpendicular to the tangent line.
What are some real-world applications of tangent lines?
Tangent lines have numerous applications in engineering, design, and geometry. For example, they are used to design gears, calculate the trajectory of projectiles, and solve geometric problems involving circles.