Examples of redox and metathesis reactions – Embark on a captivating exploration of chemical reactions as we delve into the realm of redox and metathesis reactions. These fundamental processes shape our understanding of chemical transformations and play a pivotal role in countless applications across diverse fields.
From the intricate dance of electron transfer in redox reactions to the elegant exchange of atoms in metathesis reactions, this discourse unveils the mechanisms, similarities, and differences between these two fascinating reaction types, equipping you with a comprehensive understanding of their significance in the chemical world.
Redox Reactions: Examples Of Redox And Metathesis Reactions
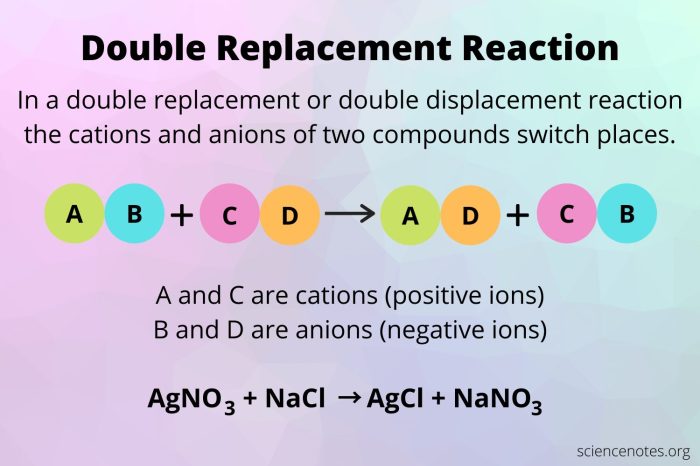
Redox reactions are chemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons between atoms, ions, or molecules. They play a crucial role in various fields, including electrochemistry, energy storage, and biological processes.
In a redox reaction, one species undergoes oxidation, where it loses electrons, while another species undergoes reduction, where it gains electrons. The oxidizing agent is the species that accepts electrons, causing the oxidation of another species, while the reducing agent is the species that donates electrons, causing the reduction of another species.
Examples of Redox Reactions
- Combustion:The burning of fuels, such as methane (CH 4), involves the transfer of electrons from the fuel to oxygen (O 2), resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide (CO 2) and water (H 2O).
- Rusting:The corrosion of iron (Fe) in the presence of oxygen and water involves the oxidation of iron to form iron oxide (Fe 2O 3).
- Electrolysis:The decomposition of water into hydrogen (H 2) and oxygen (O 2) using an electric current involves the transfer of electrons from water to the electrodes.
Metathesis Reactions
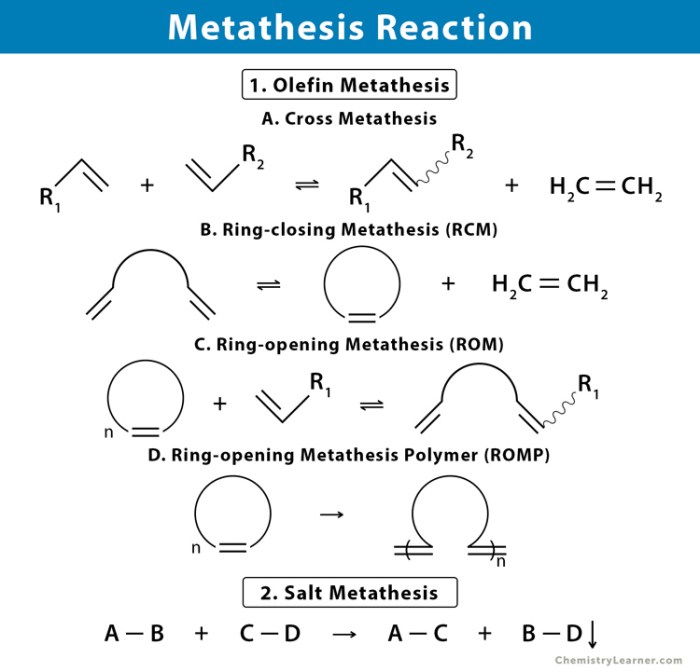
Metathesis reactions are chemical reactions in which two compounds exchange anions or cations to form two new compounds. They are commonly observed in inorganic chemistry and organometallic chemistry.
In a metathesis reaction, the cations and anions of the reactants rearrange to form new compounds with different combinations of ions. The driving force behind metathesis reactions is often the formation of a more stable or insoluble product.
Examples of Metathesis Reactions
- Precipitation reactions:The formation of an insoluble solid precipitate from the reaction of two aqueous solutions, such as the reaction of sodium chloride (NaCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO 3) to form silver chloride (AgCl) and sodium nitrate (NaNO 3).
- Acid-base reactions:The reaction of an acid and a base to form a salt and water, such as the reaction of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H 2O).
- Gas-phase reactions:The exchange of ligands between metal complexes, such as the reaction of trimethylaluminum (Al(CH 3) 3) and pyridine (C 5H 5N) to form dimethylaluminum pyridine (Al(CH 3) 2(C 5H 5N)) and methane (CH 4).
Comparison of Redox and Metathesis Reactions
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons, while metathesis reactions involve the exchange of ions. Redox reactions typically result in a change in the oxidation state of the reactants, while metathesis reactions do not.
Both redox and metathesis reactions can be used to synthesize new compounds and materials. However, redox reactions are more commonly used in electrochemistry and energy storage applications, while metathesis reactions are more commonly used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry.
| Characteristic | Redox Reactions | Metathesis Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Electron transfer | Yes | No |
| Ion exchange | No | Yes |
| Change in oxidation state | Yes | No |
| Applications | Electrochemistry, energy storage | Inorganic chemistry, organometallic chemistry |
Applications of Redox and Metathesis Reactions

Applications of Redox Reactions, Examples of redox and metathesis reactions
- Electrochemistry:Redox reactions are the basis of electrochemical cells, such as batteries and fuel cells, which convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
- Energy storage:Redox reactions are used in the development of new energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and flow batteries.
- Biological processes:Redox reactions are essential for various biological processes, such as respiration and photosynthesis.
Applications of Metathesis Reactions
- Polymer synthesis:Metathesis reactions are used in the production of polymers, such as polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Pharmaceuticals:Metathesis reactions are used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics and anti-cancer drugs.
- Catalysis:Metathesis reactions are used in the development of catalysts for various industrial processes, such as the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Advanced Concepts in Redox and Metathesis Reactions
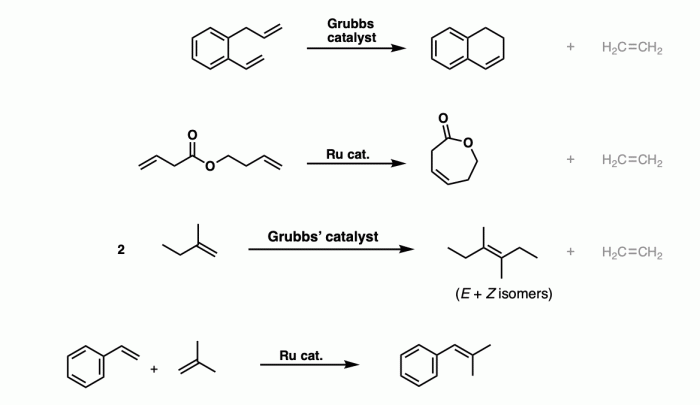
Advanced Concepts in Redox Reactions
Advanced concepts in redox reactions include electrochemistry and redox potentials. Electrochemistry deals with the study of the relationship between electrical energy and chemical reactions. Redox potentials are used to measure the tendency of a species to undergo oxidation or reduction.
Advanced Concepts in Metathesis Reactions
Advanced concepts in metathesis reactions include the use of catalysts. Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the reaction. In metathesis reactions, catalysts are often used to improve the selectivity and efficiency of the reaction.
| Catalyst | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Grubbs’ catalyst | High activity and selectivity | Expensive |
| Hoveyda-Grubbs’ catalyst | High functional group tolerance | Less active than Grubbs’ catalyst |
| Schrock’s catalyst | Tolerates a wide range of substrates | Can be unstable in the presence of air and moisture |
Detailed FAQs
What are the key characteristics of redox reactions?
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions, resulting in changes in their oxidation states.
How do metathesis reactions differ from redox reactions?
Metathesis reactions involve the exchange of atoms or groups between molecules, without any change in oxidation states.
What are some practical applications of redox reactions?
Redox reactions are employed in batteries, fuel cells, and corrosion protection.
Can you provide an example of a metathesis reaction used in industry?
Metathesis reactions are used in the production of plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene.