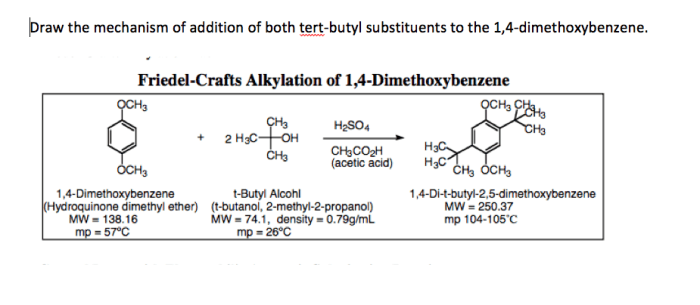
Provide a systematic name of the following compound below, a topic that captivates the minds of chemistry enthusiasts. This systematic approach to naming organic compounds, guided by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), unveils the intricacies of molecular structures, enabling chemists to communicate precisely and efficiently.
Delving into the realm of functional groups, we uncover the profound influence they exert on a compound’s properties and reactivity. These functional groups, acting as molecular beacons, guide us in identifying the parent chain, the backbone of the compound’s structure.
Systematic Nomenclature of Organic Compounds: Provide A Systematic Name Of The Following Compound Below
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established guidelines for naming organic compounds in a systematic and unambiguous manner. These guidelines ensure that each compound has a unique and descriptive name that accurately reflects its structure and properties.
The systematic naming of organic compounds involves several key principles:
1. Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that impart characteristic properties and reactivity to organic compounds. The presence of a functional group determines the compound’s classification and its chemical behavior.
- Alcohols (-OH)
- Aldehydes (-CHO)
- Ketones (-CO-)
- Carboxylic acids (-COOH)
- Esters (-COOR)
2. Parent Chain Selection, Provide a systematic name of the following compound below
The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the compound. It forms the basis of the compound’s name and determines the suffix used.
- For alkanes: -ane
- For alkenes: -ene
- For alkynes: -yne
3. Numbering the Parent Chain
The parent chain is numbered to indicate the position of functional groups and substituents. The numbering starts from the end of the chain closest to the functional group or the point of attachment of the substituent.
4. Identifying and Naming Substituents
Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain. Substituents are named using prefixes that indicate their structure and number.
- Methyl (-CH 3)
- Ethyl (-CH 2CH 3)
- Isopropyl (-CH(CH 3) 2)
5. Constructing the Systematic Name
The systematic name of an organic compound is constructed by combining the name of the parent chain, the names of the substituents, and the numbers indicating their positions. Hyphens, commas, and parentheses are used to create a clear and unambiguous name.
6. Special Cases
IUPAC nomenclature also includes special rules for handling exceptions and special cases, such as branched chains, multiple functional groups, and complex substituents.
- Branched chains are named using prefixes like “iso-” and “neo-” to indicate the position of the branch.
- Multiple functional groups are named in order of their seniority, with the highest priority group receiving the primary suffix.
- Complex substituents are named using brackets and prefixes to describe their structure.
Top FAQs
What is the significance of systematic naming in organic chemistry?
Systematic naming provides a standardized and unambiguous way to identify and describe organic compounds, facilitating communication and comprehension among chemists.
How do functional groups influence the properties of a compound?
Functional groups, such as alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones, impart characteristic chemical and physical properties to compounds, influencing their reactivity, solubility, and other attributes.
What are the key steps involved in providing a systematic name for a compound?
The systematic naming process involves identifying functional groups, selecting the parent chain, numbering the parent chain, identifying and naming substituents, and constructing the systematic name.